———–by Isaac Newton “a letter to Robert Hooke”
In addressing the question of who invented the incandescent lamp, historians Robert Friedel and Paul Israel list 22 inventors of incandescent lamps prior to Joseph Swan and Thomas Edison. According to Wikipedia .
Early pre-commercial research
In 1802, Humphry Davy had what was then the most powerful electrical battery in the world at the Royal Institution of Great Britain.
In 1835, James Bowman Lindsay demonstrated a constant electric light at a public meeting in Dundee, Scotland.
In 1840, British scientist Warren de la Rue enclosed a coiled platinum filament in a vacuum tube and passed an electric current through it.
In 1841, Frederick de Moleyns of England was granted the first patent for an incandescent lamp, with a design using platinum wires contained within a vacuum bulb.
In 1845, American John W. Starr acquired a patent for light bulb involving the use of carbon filaments.
In 1851, Jean Eugène Robert-Houdin publicly demonstrated incandescent light bulbs on his estate in Blois, France. His light bulbs are on permanent display in the museum of the Château de Blois.
In 1872, Russian Alexander Lodygin invented an incandescent light bulb and obtained a Russian patent in 1874. He used as a burner two carbon rods of diminished section in a glass receiver, hermetically sealed, and filled with nitrogen, electrically arranged so that the current could be passed to the second carbon when the first had been consumed.
Heinrich Göbel, who used the name Henry Goebel in the USA, made a claim in 1893 during litigation over Edison’s light bulb patent that, back in 1854, he had designed the first incandescent light bulb with a thin carbon-filament: a carbonized bamboo filament of high resistance, platinum lead-in wires in an all-glass envelope, and a high vacuum created by the process invented by Torricelli, and that in the following years he developed what many call the first practical incandescent light bulb.
In North America, parallel developments were taking place. On July 24, 1874, a Canadian patent was filed by a Toronto medical electrician named Henry Woodward and a colleague Mathew Evans. They built their lamps with different sizes and shapes of carbon rods held between electrodes in glass cylinders filled with nitrogen.
Commercialization
Joseph Swan (1828–1914) was a British physicist and chemist. In 1850, he began working with carbonized paper filaments in an evacuated glass bulb. By 1860, he was able to demonstrate a working device but the lack of a good vacuum and an adequate supply of electricity resulted in a short lifetime for the bulb and an inefficient source of light. By the mid-1870s better pumps became available, and Swan returned to his experiments.
Thomas Edison began serious research into developing a practical incandescent lamp in 1878. Edison filed his first patent application for “Improvement In Electric Lights” on October 14, 1878.After many experiments with platinum and other metal filaments, Edison returned to a carbon filament. The first successful test was on October 22, 1879, and lasted 13.5 hours.
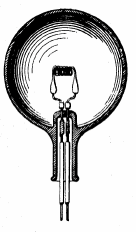
(U.S. Patent 0,223,898 by Thomas Edison for an improved electric lamp, January 27, 1880)
Environmental Protection Challenge
The effectiveness of an electric lighting source is determined by two factors: the visibility rate of electromagnetic radiation , and the converting rate from electric power into electromagnetic radiation.
Approxiamtely 90% of power consumed by an incandescent lamp is emitted as heat, rather than visible light.
The chart bellow list the Lumen Efficiency of 1000 hours lifespan Incandescent lamp.
| Type | Overall luminous efficiency | Overall luminous efficacy (lm/W) |
|---|---|---|
| 40 W tungsten incandescent | 1.9% | 12.6 |
| 60 W tungsten incandescent | 2.1% | 14.5 |
| 100 W tungsten incandescent | 2.6% | 17.5 |
| glass halogen | 2.3% | 16 |
| quartz halogen | 3.5% | 24 |
| high-temperature incandescent | 5.1% | 35 |
| ideal black-body radiator at 4000 K (or a class K star like Arcturus) | 7.0% | 47.5 |
| ideal black-body radiator at 7000 K (or a class F star like Procyon) | 14% | 95 |
| ideal monochromatic 555 nm (green) source | 100% | 683 |
As development of lighting technology, Incandescent lamp is gradually replaced by other types of lighting sources in many applications:
Halogen Lamp
Fluorescent Lamp
Compact Fluorescent Lamp
Metal Halide Lamp
Cold Cathode Fluorescent lamp
External Electric Fluorescent Lamp
Led Emitting Diode ( LED Lamp)